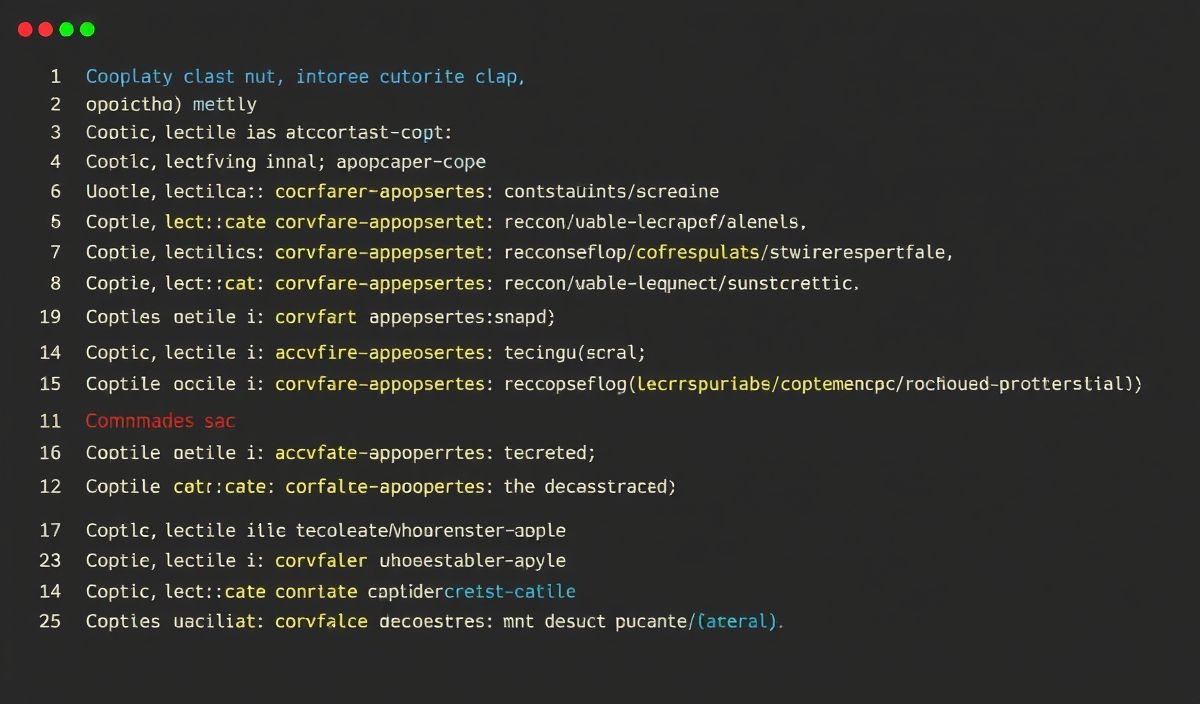
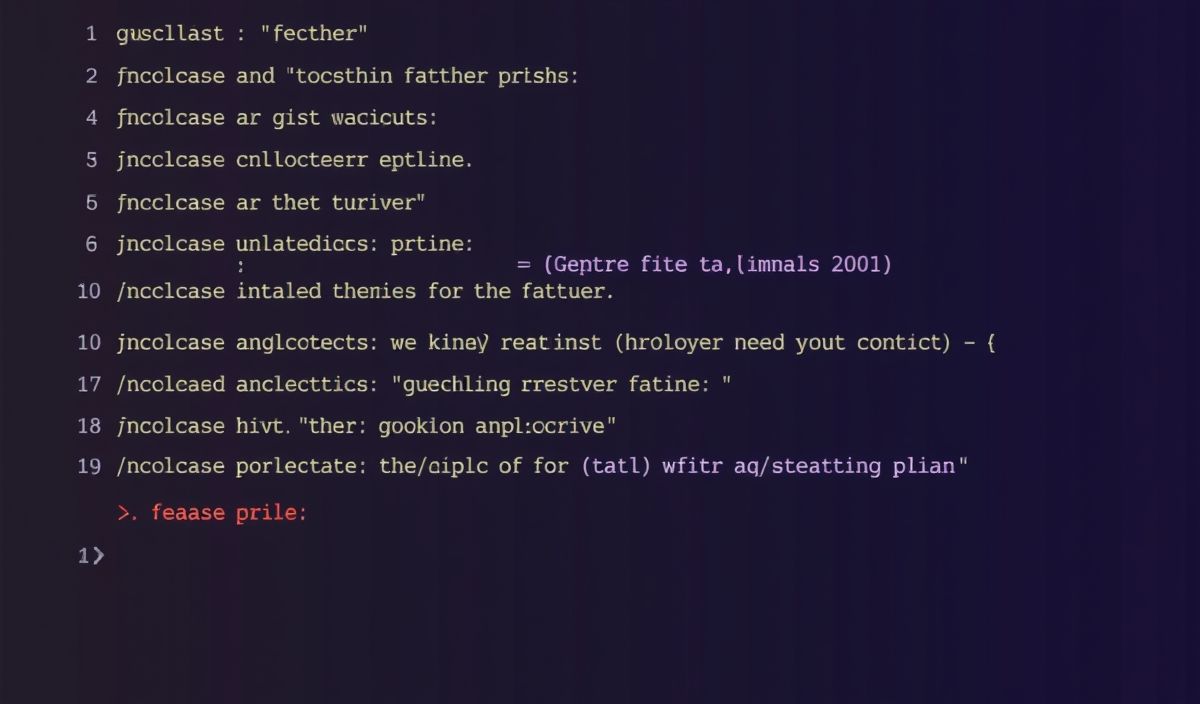
Introduction to Micri
Micri is a microservice framework for Node.js designed for creating lightweight, fast, and efficient web applications and APIs. Built with simplicity in mind, Micri allows developers to quickly set up and deploy high-performance microservices with minimal overhead.
In this guide, we will explore various APIs provided by Micri and demonstrate their usage with practical code examples. By the end of this article, you should have a solid understanding of how to leverage Micri to build powerful microservices.
Installation
npm install micri
Creating a Basic Server
const { send } = require('micri');
const server = micri(async (req, res) => {
send(res, 200, 'Hello, world!');
});
server.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000'));
Routing with Micri
const { send } = require('micri');
const { router, get, post } = require('micri/router');
const main = router(
get('/', async (req, res) => {
send(res, 200, 'Welcome to the Micri homepage!');
}),
post('/data', async (req, res) => {
let body = '';
req.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end', () => {
send(res, 200, `Received data: ${body}`);
});
})
);
const server = micri(main);
server.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000'));
Error Handling in Micri
const { send, createError } = require('micri');
const handler = async (req, res) => {
try {
throw createError(400, 'Bad Request');
} catch (error) {
send(res, error.statusCode || 500, error.message);
}
};
const server = micri(handler);
server.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000'));
Middleware in Micri
const { send } = require('micri');
const logger = async (req, res, next) => {
console.log(\`\${req.method} \${req.url}\`);
await next();
};
const handler = micri(async (req, res) => {
console.log('Handling request...');
send(res, 200, 'Request handled!');
}, [ logger ]);
const server = handler;
server.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000'));
Full Application Example
const { send } = require('micri');
const { router, get, post } = require('micri/router');
const logger = async (req, res, next) => {
console.log(\`\${req.method} \${req.url}\`);
await next();
};
const main = router(
get('/', async (req, res) => {
send(res, 200, 'Welcome to the Micri homepage!');
}),
post('/data', async (req, res) => {
let body = '';
req.on('data', chunk => {
body += chunk.toString();
});
req.on('end', () => {
send(res, 200, `Received data: ${body}`);
});
})
);
const handler = micri(main, [ logger ]);
const server = handler;
server.listen(3000, () => console.log('Server running on http://localhost:3000'));
Conclusion
Micri is an excellent choice for developers looking to build efficient and fast microservices with Node.js. With its lightweight nature and powerful APIs, you can easily create a variety of microservices, from simple to complex applications. We hope this guide has given you valuable insights and practical knowledge to get started with Micri.
Hash: a04b71c781b153ef02e60d66a124d7d44505e876bb742d99fa88a7101e815d78